Introduction
Anal fissures are tears or fissures in the anal canal's lining of the anal canal that result in discomfort and rectal bleeding during bowel movements. Anal trauma, especially when straining to pass solid faces, can cause them, and they can heal quickly or slowly. Stool softeners, fiber supplements, topical ointments, and, in certain circumstances, surgery are available as treatment.1 An additional element of the fixed combination, a common local anaesthetic for anal fissures and symptomatic haemorrhoids, is lidocaine.2 Lidocaine and nifedipine work in complimentary ways when combined. Clinical trials have demonstrated that the anal sphincter's smooth muscle relaxed as a result of nifedipine calcium channel blockage, reducing pain during haemorrhoidectomy 3, 4. When administered anorectally, this fixed combination was safe, effective, and associated with very few adverse effects, according to clinical tests involving patients with hemorrhoidal thrombosis and anal fissures.5 Topical nifedipine and diltiazem showed impressive effectiveness, with a healing rate of up to 95% for nifedipine and 67% for diltiazem. Diltiazem and nifedipine are calcium channel blockers with the greatest evidence in favor of topical use. They are made on the spot using bases of cream, gel and ointment. Research has indicated that calcium channel blockers use topically and orally relax the internal anal sphincter, hence reducing the anal resting pressure. While calcium channel blockers and glyceryl trinitrate were tested for their efficacy in treating anal fissures, nifedipine treatment resulted in high healing rates (89%) that were similar to previously reported rates in (95%).6 Local anaesthetic, which is another part of the fixed combination lidocaine, is typically used to treat symptomatic haemorrhoids and anal fissures.7 Lidocaine (LID) has the formula 2-(di-ethyl amino)-N-(2,6-di-methylamino) acetamide is a local anaesthetic that has strong anticonvulsant and antiarrhythmic properties. It has sedative, analgesic, and anticonvulsant properties in addition to being a CNS depressant. Nifedipine (NIF) is 3,5-di-methyl-2,6-di-methyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-di-hydropyridine-3,5-di-carboxylate is a strong vasodilator that acts by antagonistically interacting with calcium. It is a helpful blood pressure-lowering antianginal drug. On February 26, 2009 (by CDSCO).8, 9, 10 The validation has been performed as per ICH Q2(R1) guidelines. A literature survey reveals that lidocaine has been estimated using a number of techniques, including UV spectroscopy, RP-HPLC, HPLC-MS/MS spectrometry, and stability-indicating techniques HPLC, Ultra performance Liquid chromatography (UPLC), MS/MS and UV spectroscopy are techniques for estimating nifedipine, the simultaneous estimation of lidocaine and nifedipine has been done in several investigations using a UV spectroscopic method. Proposed RP-HPLC method includes a separation of drugs at less time.11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19
Objectives
To select the detection wavelength for simultaneous estimation of Lidocaine and Nifedipine
To develop the optimum Mobile phase for the simultaneous estimation of Lidocaine and Nifedipine
To validated the developed method as per ICH Q2 (R1) guidelines for the simultaneous estimation of Lidocaine and Nifedipine.
Material and Methods
Chemicals and reagents
API of Nifedipine was purchased from Mumbai, API of lidocaine was a gift from Valsad, Gujarat. HPLC-grade water and methanol has been purchased from India.
Instrumentation
Thermo Ultimate 3000 (chromeleon software) with a PDA detector C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) was used. Weighing Balance (XB-220A) Precisa. Digital ultra-sonication cleaner (CD-4820) by Euipton Digital pH meter (S-90) Systonic. UV-Visible spectrophotometer (CARRY-60) Agilent.
Selection of wave length
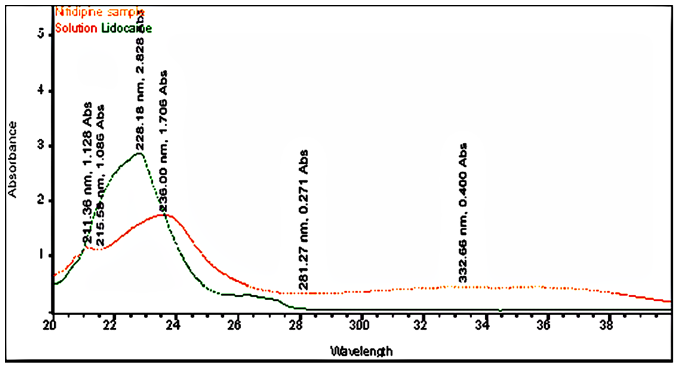
Lidocaine and Nifedipine are soluble in methanol, The standard stock solution 10 µg/mL of lidocaine and nifedipine was prepared in methanol, and the solution scanned in the UV range of 200-400 nm using methanol as a blank, and the UV spectrum was obtained. The absorbance maximum was found to be 236 nm and selected as the detection wavelength for further analysis.
Sample preparation
Lidocaine (LID) and Nifedipine (NIF) standard stock solution were made separately by dissolving the required quantity of each substance in methanol. These solutions were subsequently diluted to create concentration LID at 150 µg/mL and NIF at 30 µg/mL. A quantity equal to 150 mg NIF and 30 mg of LID was precisely weighed and then put to a volumetric flask of 100 ml for the cream sample that included both LID (1.5 %w/w) and NIF (0.3 %w/w). The mixture was then swirled for 30 min and sonicated for 15 min to ensure that the compounds were well dissolved before 5 ml of methanol was infused into the flask. To create a homogeneous solution, 100 ml of methanol were added to the capacity to make it larger. A 0.45 µ nylon syringe filter was used to filter the mixture.
Chromatographic Conditions
Stationary Phase: Thermo Ultimate (chromeleon software) C18 (150 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm)
Mobile phase: methanol and water (80:20% v/v)
Flow rate: 1 mL/min
Wavelength: 236 nm
Run time: 10 min.
Table 1
Result of system suitability test for lidocaine and nifedipine
Table 2
Result of LOD and LOQ test for lidocaine and nifedipine
Table 3
Accuracy studies for lidocaine and nifedipine result
|
% Level |
Amount present (µg/mL) |
Amount recovered |
% Recovery |
|||
|
LID |
NIF |
LID |
NIF |
LID |
NIF |
|
|
50 % |
15 |
3 |
15.01 |
3.01 |
100.10 |
100.51 |
|
100 % |
30 |
6 |
30.19 |
6.03 |
100.66 |
100.58 |
|
150 % |
45 |
9 |
45.18 |
8.82 |
100.42 |
98.11 |
Table 4
Result of precision studies for lidocaine and nifedipine
Table 5
Result of robustness studies for lidocaine and nifedipine
Method Validation
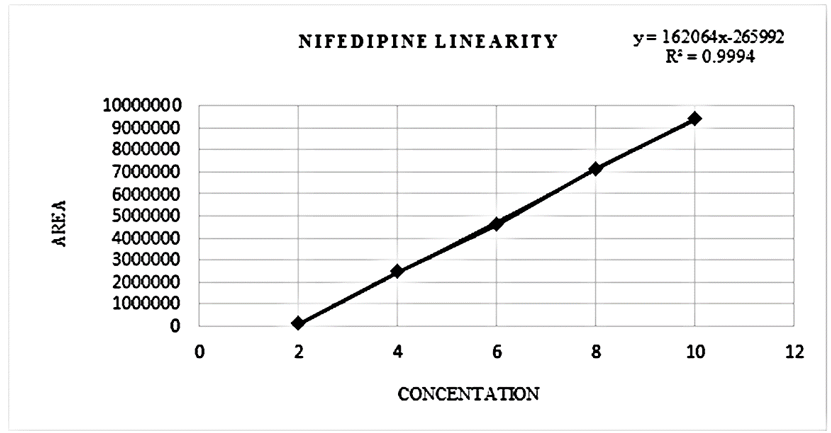
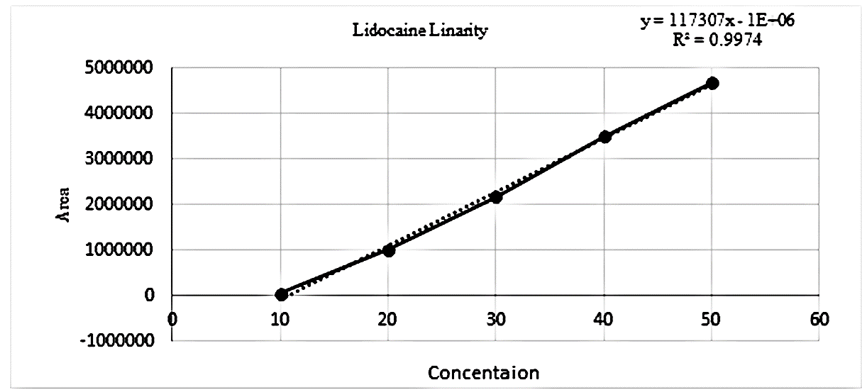
The validation of proposed methods involved method development, optimization, and adherence to the guidelines specified in ICH Q2 (R1). Following these guidelines ensures the specificity, accuracy, a nd reproducibility of the method, allowing for robustness and credible analytical results.20, 21 The Linearity has been performed by five injections of standard nifedipine and lidocaine at concentration range of 2-10 µg/mL and 10-50 µg/mL, respectively. Accuracy study has been performed at 50%, 100% and 150%. A study of the precision of the developed method was conducted on both an intra-day and inter-day basis with lidocaine and nifedipine at three distinct concentration levels. The concentrations used were 15 μg/ml, 30 μg/ml, 45 μg/ml, 3 μg/ml, 6 μg/ml, and 9 μg/ml. Robustness has been performed by changing flow rate, temperature and wavelength. Assay has been performed in a sample solution containing 150 µg/mL of lidocaine and 30 µg/mL of nifedipine.
Results and Discussion
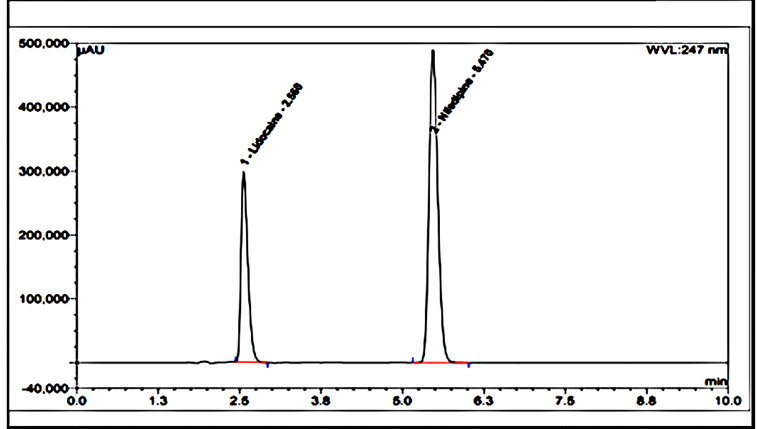
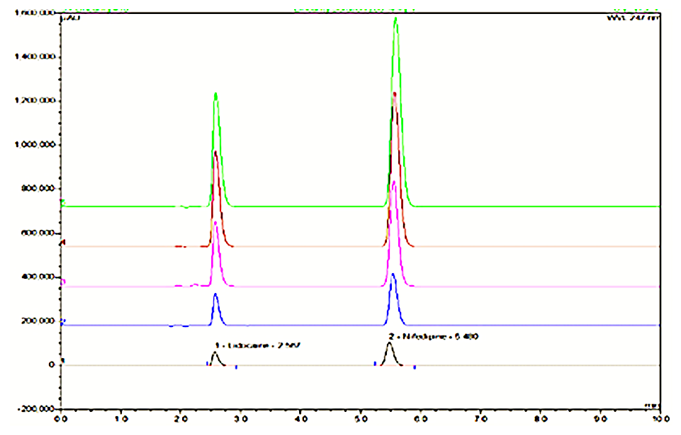
There is an HPLC method reported. I decided to develop a new method by modifying the reported method. Methanol: Water (80:20% v/v) was chosen because it provided peaks with separation of lidocaine and nifedipine. The drugs UV spectra (λ Max) were analysed in the wavelength range of 200-400 nm, and the response for optimization was compared. A careful evaluation of both drugs revealed that 236 nm was the optimal wavelength for adequate sensitivity. The findings obtained the specified requirements, with a resolution value greater than 2, a tailing factor less than 1, and an RSD less than 2. Lidocaine and nifedipine were evaluated using the system suitability test. The total theoretical plates (N) for lidocaine and nifedipine were 5648 and 15000, respectively. These results show effective chromatographic separation and decent peak shape because they are both above the permissible limit of 2000. Lidocaine and nifedipine had tailing factors of 1.356 and 1.094, respectively. Both of these numbers fall below the 2.0 limit, indicating peaks that are symmetrical. The results of the system suitability test for lidocaine and nifedipine are described in Table 1. LOD and LOQ for lidocaine and nifedipine were found to be 0.04 and 0.15 for lidocaine and 0.03 and 0.10 for nifedipine, respectively. The results of LOD and LOQ for lidocaine and nifedipine are described in Table 2 . Standard solutions containing lidocaine (10-50g/ml) and nifedipine (2-10g/ml) were tested to determine linearity. The results of linearity for lidocaine and nifedipine are described in figures 4, 5, and 6. Lidocaine and nifedipine % RSD and % recovery at each concentration level revealed that they were found to be within the range. A range of 99.99% to 100% has been obtained for both lidocaine and nifedipine recovery rates. The results of accuracy are described inTable 3. The % RSD has determined at each concentration level being below 2%. Indicates that the development method exhibits high precision, as the RSD value is within the acceptable range. In the robustness study, RSD was found to be less than 2%. In this case, we found the content % to be between 99% and 100%.