Introduction
Fenticonazole Nitrate (FTZ) is an Imidazole antifungal drug used in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. It is active against the range of organism including dermatophyte pathogens, Malassezia furfur, and Candida albicans.1 The interesting mechanism of action of Fenticonazole is inhibition of the secretion of protease acid by Candida albicans, damage to the cytoplasmic membrane; and by blocking cytochrome oxidases and peroxidises 2 Fenticonazole Nitrate chemically is 1-[2(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2 {[4 (phenyl sulfanyl) phenyl]methoxy}ethyl]1H-imidazole. The chemical structure of Fenticonazole Nitrate is shown in Figure 1 Fenticonazole is official reported in EP with their characteristics, Identification test, Assay and Impurity detection.3 Some literature of Fenticonazole is also exist in Merck index and Martindale.4, 5 The information of related substance with their identification test are reported in BP.6 In literature, few liquid chromatography procedures have been reported for the analysis of Fenticonazole Nitrate.7, 8, 9, 10, 11 The present UV-Spectrophotometric methods were designed for estimation of Fenticonazole Nitrate using Methanol as a solvent. The current works emphasize simple, precise, sensitive and effective UV Spectroscopy method for estimation of Fenticonazole Nitrate in bulk and in-Vaginal capsules. The method was validated as per ICH guidelines.
Experimental
Preliminary solubility studies and selection of solvent
Solubility of FTZ was found in Methanol and Dimethylformamide (DMF). The Fenticonazole Nitrate is completely soluble in methanol. So for further study Methanol is used as a solvent.
Preparation of stock standard solution
Stock standard solution of FTZ was prepared by dissolving accurately weighed 10mg of FTZ into 100ml of Methanol, to obtain concentration of 100µg/mL. sonicated for 5 min. The working standards were prepared by dilution of the stock standard solution.
Determination of λ max and calibration curve
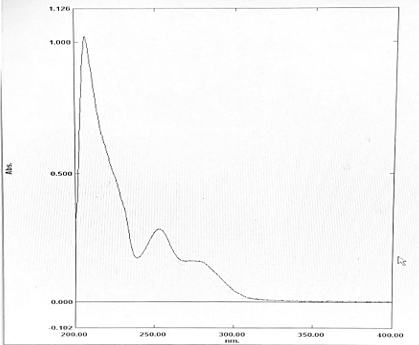
A fixed volume of 1.0mL of FTZ from stock solution was transferred to 10mL volumetric flask, diluted to mark with Methanol to obtain concentration of 10µg/mL. The resultant solution was scanned in UV range (400-200nm) in 1.0cm cell against solvent blank. The spectrum showed an absorption maximum at 253nm.
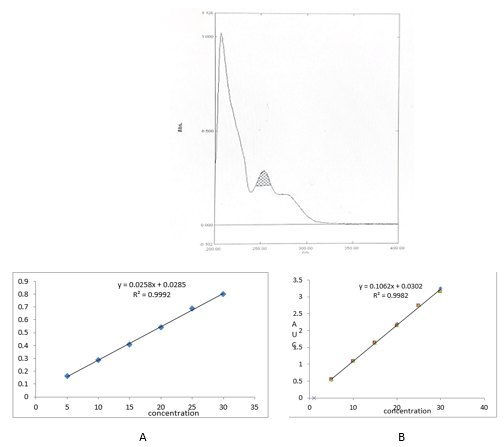
In Method I absorbance at 253nm was considered for analysis while for Method II two wavelengths 242-262 nm were selected for determination of Area under Curve [AUC]. Optical Characteristics of FTZ presented in.Table 1. Zero order UV-spectrum showing maximum absorbance and AUC are shown in.Figure 2
Table 1
Optical characteristics and linearity of fenticonazole nitrate
An appropriate volume of stock solution in the range of 0.5–3.0mL were transferred in series of 10mL volumetric flask, volume was made up to 10mL with Methanol to get concentration of 5–30µg/mL and absorbance was measured at 253nm (method I) and Zero order- AUC was recorded in between the wavelength range of 242-262 nm (Method II) against the blank. Calibration curves were prepared by plotting concentration versus absorbance and AUC as shown in.Figure 3
Analysis of Capsule formulation
Ten capsules were accurately weighed and average weight determined, an amount of power drug equivalent to 10 mg of Fenticonazole Nitrate was transfer into 100 mL volumetric flask containing 100 ML of Methanol, sonicated for 5 min. The volume was made up to the mark with same solvent and filtered through 0.45µm Whatman filter paper. A suitable volume of solution was further diluted with Methanol to obtain concentration 20µg/mL of Fenticonazole Nitrate for tablet assay. These sample solutions were scanned at selected wavelengths in Method I and Method-II and the results were obtained. From the respected linear regression equations, the concentrations were determined. The procedure was repeated for six times and the results are shown in.Table 2
Table 2
Analysis of vaginal capsules
|
|
Label claim(mg) |
Conc (µg/mL) |
%Amount found n=6 |
±SD |
±RSD |
|
Method 1 |
600 |
20 |
100.56 |
0.5428 |
0.5406 |
|
Method 2 |
600 |
20 |
100.06 |
0.1855 |
0.1853 |
Table 3
Average of three estimates
Accuracy/Recovery Studies
To estimate the accuracy of both the proposed methods, recovery studies were executed out at 50, 100 and 150% of the test concentration as per ICH guidelines. To the pre-analyzed sample solution (10µg/ml), a known amount of drug standard was added at 50, 100 and 150% and solutions were reanalyzed by proposed methods. The experiments were performed three times at each level for each method. The results of the recovery studies are reported in the table below.
Precision
Precision of the methods were studied as intra-day, inter-day variations and repeatability. Precision was determined by analyzing the concentration of 15, 20, and 25µg/ml. To determine the degree of repeatability of the methods, statistical evaluation was carried out, and the results are reported in the table below.
Repeatability
Repeatability was determined by analyzing Fenticonazole concentration of 20µg/mL for six times and results are reported in below table.
Ruggedness
The ruggedness of the proposed method was determined by analysis of aliquots from homogenous slot by two analyst using same operational and environmental conditions and the results are reported in below table.
Sensitivity
The sensitivity of proposed methods was estimated in terms of estimating Detection Limit (DL) and Quantitation Limit (QL) which were calculated using formulae “DL = 3.3 ×N/B,” and “QL = 10 × N/B” where “N” is average standard deviation of the absorbance or peak areas of the Fenticonazole (n = 3), taken as a measure of noise, and “B” is the slope of the corresponding calibration curve.
Results and Discussion
In the present investigation, Methanol is used to enhance the aqueous solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs Fenticonazole Nitrate in bulk and in vaginal capsules. By selecting proper solvent. For the solubility studies, different solvent was tried but optimum solubility was achieved in Methanol. In Method I and II, linearity of Fenticonazole Nitrate was found to be in the range of 05 - 30µg/mL, with correlation coefficient (r2 > 0.99). Marketed brand of Vaginal capsules were analyzed. The amounts of Fenticonazole Nitrate determined by ‘Method I’ and Method II was found to be 100.56% and 100.06, respectively. In both these methods, precision was studied as repeatability, inter and intra-day variations at three different concentrations of Fenticonazole Nitrate and % RSD was found to be less than 2. The accuracy of method was determined by calculating mean percentage recovery. It was determined at 50, 100 and 150% level and % recovery was found to be in the range 100.80% - 100.93% and 100.37% – 99.94% for method I and II respectively. The ruggedness of the methods was studied by two different analysts using the same operational and environmental conditions and % RSD found to be less than 2. DL and QL were found to be 0.3117µg/ml and 0.9448 µg/ml, respectively for Method I and DL and QL were found to be 0.3260µg/ml and 0.9878µg/ml respectively for Method II indicating adequate sensitivity of the methods.
Conclusion
The proposed methods for analysis of Fenticonazole Nitrate in pharmaceutical formulations are ecofriendly; simple, precise and rapid so can be employed for routine analysis. From the proposed methods, we conclude that there is a good scope for other poorly water-soluble drugs to get solubilized by using organic solvents.