Introduction
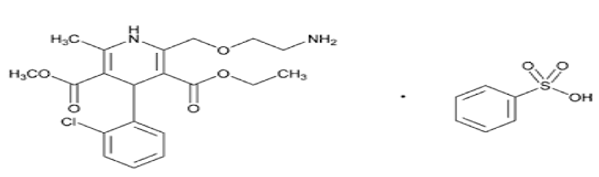
Amlodipine is a synthetic dihydropyridine and a calcium channel blocker with antihypertensive and antianginal properties. It is a dihydropyridine, a member of monochlorobenzenes, an ethyl ester, a methyl ester and a primary amino compound. Chemical name of amlidipine is 3-O-ethyl 5-O-methyl 2-(2-aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate benzene sulphonate (Figure 1). 1, 2 Amlodipine act by blocking voltage-sensitive calcium channels (L-type). Amlodipine slow conduction in the SA and AV nodes where action potential propagation depends on slow inward Ca2+ current, slowing the heart and terminating SVT by causing partial AV block. It shortens the plateau of the action potential and reduces the force of contraction. Reduced Ca2+ entry reduces after depolarization and thus suppresses premature ectopic beats.3, 4, 5
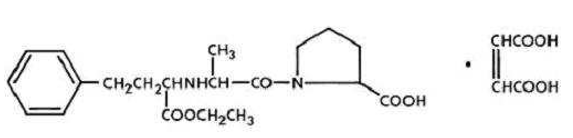
Enalapril is a prodrug which is hydrolysed in the body to Enalaprilate, which is an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). It is indicated for treatment of hypertension, treatment of symptomatic heart failure and prevention of symptomatic heart failure in patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction (ejection fraction <35%). Chemically it is ((S)-1-{N-[1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]-Lalanyl}-L-proline, (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) (Figure 2), a derivative of two amino-acids, L-alanine and L-proline. It is a white to off-white crystalline, odourless powder which melts in the range of 143–144◦C. ACE is a peptidyl dipeptidase that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin-I to the vasoconstrictor substance, angiotensin-II, which stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex. Blocking the conversion of the angiotensin I to the angiotensin II, leads to a reduction in vasopressin activity and a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance.6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
Materials and Methods
Reagents and chemicals
All solvents used were of HPLC grade. The reference standards of Amlodipine besylate and Enalapril maleate were obtained as gift samples from LUPIN Pharmaceutical Ltd. (Bhopal, India). The commercial fixed dose combination product Amtas E (Intas, Ahemdabad) containing Amlodipine 5 mg and Enalapril 5 mg was obtained from local pharmacy store. The solvents used were Methanol HPLC grade and Hydrochloric acid was procured from Cipla.
Preparation of standard stock solution
The standard stock solutions of AML (100μg/ml), ENA (100μg/ml) were prepared by transferring 10mg of Amlodipine besylate and 10mg of Enalapril maleate respectively in 100ml Volumetric flasks. The volume was made upto the mark using mobile phase (methanol : 0.1N HCl [1:1]). The solutions were sonicated for 15 min and filtered through Whatmann filter paper.
Preparation of sample solution
Twenty tablets were weighed accurately, their average weight was determined and powdered. The powder of the tablets equivalent to 5 mg of AML and 5 mg of ENA was transferred into 50 ml volumetric flask. 25 ml of methanol : 0.1N HCl (1:1) was added into the volumetric flask and sonicated for 15 min to effect complete dissolution of the drugs. Then the volume was made upto the mark with mobile phase. The solution was filtered through the Whatmann filter paper and the aliquot portion of the filtrate was further diluted to get the final concentration of 100µg/ml. 10μl of the above solution was injected into the HPLC under the set chromatographic conditions.
Results and Discussion
Figure 3
Chromatogram Report of Amlodipine besylate & Enalapril maleateFor Amlodipine besylate RT = 7.6 min For Enalapril maleate RT = 3.2 min

Method validation
Validation of any analytical method shall be done to establish by laboratory studies, that the performance of the method meet the requirement for the intended analytical application. The method was validated according to ICH guidelines to study linearity, accuracy and precision.13, 14, 15
Linearity
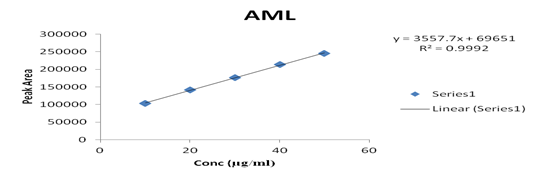
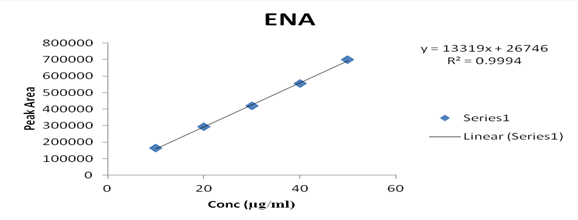
Several aliquots of standard solutions of AML and ENA were taken in different 10 ml volumetric flasks and the volume was made upto the mark with mobile phase such that final concentration of AML and ENA were 10-50 μg/ml, respectively. Evaluation was performed using the UV-Vis detector at 218 nm, peak area recorded for all the peaks, results are displayed in Table 2. Calibration curve was plotted as concentration against peak area as shown in graph 2 & 3. The slope and intercept value for calibration curve were y = 3557.7x + 69651 (R² = 0.9992) for AML, y = 13319x + 26746 (R² = 0.9994) for ENA
Recovery
Accuracy of the method was calculated by recovery studies at three levels (80%, 100% and 120%) by standard addition method. The accuracy was expressed as the percentage of the analyte recovered. Accuracy of proposed method was checked as per ICH guidelines. For AML, tablet powder equivalent to 5 mg AML was taken individually into three different 100 ml volumetric flasks and then 8 mg (80%), 10 mg (100%) and 12 mg (120%) of standard AML were added to each of the volumetric flasks. After that 25 ml of the mobile phase [methanol : 0.1N HCl (1:1)] was added to each of the volumetric flask and sonicated for 5 min. The solutions were then filtered and 1 ml of the filtrate from each was taken in 10 ml volumetric flasks individually and diluted upto the mark with mobile phase. The solutions were injected in triplicates into the chromatographic system and the peak area were evaluated to give Percent Recovery and Standard deviation. Similar procedure was repeated for other drug.
Table 3
Precision
|
Drug |
Intraday |
Interday |
||
|
% Obtained ± SD |
%RSD |
% Obtained ± SD |
%RSD |
|
|
Amlodipine Besylate |
103.72 ± 0.87 |
0.85 |
107.51 ± 1.01 |
0.94 |
|
Enalapril Maleate |
103.54 ± 0.88 |
0.86 |
105.35 ± 1.008 |
0.96 |
Robustness: The robustness of the proposed method was verified by varying the solvent ratio in the mobile phase, flow rate and wavelength range. Sample solutions were injected as 10μl injection into the chromatographic system. The parameters studied were peak area and found their standard deviation & % RSD.
Limit of detection and Limit of quantification: The LOD and LOQ of the proposed method were determined by progressively injecting lower concentrations of the standard solutions under the set chromatographic conditions. The results obtained are displayed in Table 5.
L.O.D. = 3.3(SD/S)
L.O.Q. = 10(SD/S)
Where, SD = Standard deviation of the response,
S =Slope of the calibration curve. The slope S may be estimated from the calibration curve of the analyte.
Table 5
System suitability parameters
Conclusion
The developed method gives good resolution between Amlodipine besylate and Enalapril maleate with short analysis time. The method is simple, accurate, rapid, precise and can be easily used for routine analysis of these drugs without involving any complicated sample preparation.