- Visibility 88 Views
- Downloads 22 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpca.2024.041
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Polymeric innovations in drug delivery: Enhancing therapeutic efficacy
- Author Details:
-
Jayapal Reddy Gangadi *
-
Pavan Kumar Kokkula
-
M. Kannadasan
Introduction
Drug delivery overview
Drug delivery is the process of administering pharmaceutical compounds to produce a therapeutic effect in humans or animals. The effectiveness of treatment depends on delivering the medication to the right location in the body, at the right time, and in the correct dosage. Drug delivery technologies are specifically designed to alter how a drug is released, absorbed, distributed, and eliminated within the body. These adjustments aim to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential side effects. Additionally, these technologies improve patient compliance by making medications easier to use and more effective over extended periods. Ultimately, drug delivery systems play a critical role in ensuring the success of medical treatments.[1], [2]
Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Innovative drug delivery systems provide various approaches to enhance the efficiency of drug administration. Some key solutions include:[3]
Oral Drug Delivery Systems
Parenteral and Implantable Drug Delivery Systems
Pulmonary and Nasal Drug Delivery
Transmucosal Drug Delivery
Transdermal and Topical Drug Delivery
Delivery of Proteins and Peptides
Drug Delivery Pipelines and Partnerships
Role of Polymers in Drug Delivery
Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating units, characterized by their long chains and diverse functional groups. Their ability to blend with materials of varying molecular weights makes them highly adaptable. In pharmaceutical applications, polymers play an essential role in enhancing the performance and delivery of drugs. Recent advances in polymer science have enabled the development of innovative drug delivery platforms. By carefully engineering the surface and bulk properties of polymers, researchers can create materials tailored to specific drug delivery needs, ultimately improving treatment outcomes and patient adherence.
List of polymers used in oral drug delivery [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
Natural polymers
Protein-based Polymers: Collagen, Albumin, Gelatin
Polysaccharides:
Alginate
Chitosan
Dextran
Gums
Hyaluronic Acid
Starch
Cellulose
Others: Polyisoprenoids
Synthetic polymers
Biodegradable Polymers:
Polyester:
Poly Lactic Acid
Poly Glycolic Acid
Poly Hydroxybutyrate-co-Valerate (PHBV)
Polycaprolactone (PCL)
Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)
Poly anhydride
Poly Sebacic Acid
Poly Adipic Acid
Various Copolymers
Others: Polyanhydrides
Non-Biodegradable Polymers:
Silicones: Siloxanes
Cellulose Derivatives: Cellulose Acetate Propionate, Cellulose Acetate Butyrate
Other Synthetic Carbonates: Polycarbonate
Acrylics: Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA , Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA)
Others
Vinyl Chloride Polymer and Copolymers, Styrene Acrylonitrile Polymer (SAN) Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene Polymer (ABS), Polystyrenes
Recent technological advancements in drug delivery include chemical modification of drugs, carrier-based delivery systems, and drug entrapment within polymeric matrices or pumps placed in specific bodily compartments. These innovations enhance drug therapy efficacy and improve human health. The use of polymeric materials in novel drug delivery systems has garnered significant scientific interest. [9], [10]
The application of polymers for medical purposes is rapidly expanding. Polymers are now integral to various biomedical fields, including drug delivery systems, tissue engineering scaffolds, medical device implants, artificial organs, prosthetics, ophthalmology, dentistry, bone repair, and more. [11] Polymers are essential for controlling drug release rates from formulations, offering unique properties unmatched by other materials. The progress in polymer science has resulted in the creation of innovative drug delivery systems. Proper consideration of surface and bulk properties is crucial in designing polymers for diverse drug delivery applications. [12], [11]
Advancements in drug delivery technologies, such as chemical drug modifications, carrier-based delivery, and drug encapsulation within polymer matrices or pumps, have greatly enhanced therapeutic effectiveness and improved patient outcomes. [13] Polymer chemists, chemical engineers, and pharmaceutical scientists are actively developing controlled delivery systems to release bioactive agents with precision. Biodegradable polymers are especially valued in biomedical applications due to their compatibility with biological systems and ability to degrade safely over time. These polymers are frequently used in implants, where they are expected to function reliably over long periods, contributing to more effective treatments with fewer side effects and greater patient comfort. [14]
Polymers play a versatile role in pharmaceutical formulations, serving as binders in tablets, viscosity enhancers in liquids, and emulsifying agents in suspensions. They are also applied as film coatings to mask unpleasant drug tastes, improve stability, and control drug release. These materials enable functions such as taste masking, controlled release (including extended, pulsatile, and targeted delivery), improved stability, and enhanced bioavailability. One example is monolithic delivery devices, where a drug is dispersed within a polymer matrix and released gradually through diffusion. The release rate from such systems depends on factors like the initial drug concentration and the relaxation of polymer chains, ensuring a sustained therapeutic effect. [15]
Polymers can also be modified to expand their applications. Adjusting water solubility by increasing chain length, cross-linking, or incorporating hydrophobic or hydrophilic copolymers creates materials with a wide range of properties. These modifications enable polymers to perform various drug-enhancing functions, supporting more effective and targeted therapies. [16]
Functions of Polymers in Drug Delivery [17], [18]
Polymers offer several benefits in drug delivery, including:
Extending drug availability when formulated as hydrogels or microparticles
Improving biodistribution through dense nanoparticle formulations
Facilitating hydrophobic drug delivery via micelles
Targeting inaccessible areas by acting as carriers in gene therapies
Releasing drugs in response to specific stimuli for precision therapy
Polymers are produced on an industrial scale, ensuring efficient solubilization of pharmaceuticals for safe administration. Ongoing efforts focus on optimizing clinical doses and dosing schedules to improve the safety and effectiveness of treatments, reducing side effects and enhancing patient comfort.
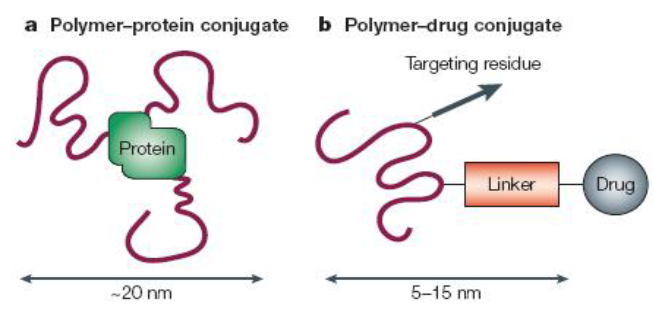
Polymer Therapeutics and PE Gylation [19], [20]
The development of polymer therapeutics has evolved significantly, with notable contributions by Davis and colleagues in the late 1970s through their work on PEGylation. This technique involves covalently attaching polyethylene glycol (PEG) to proteins or peptides to enhance their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Over the past two decades, PEGylation has become a preferred method in pharmaceutical development because PEG is non-toxic, non-immunogenic, and non-antigenic. The U.S. FDA has approved PEG for various pharmaceutical applications, including injectables, topical products, rectal preparations, and nasal formulations.[21], [22], [23]
The hydrophilic nature of PEG shields therapeutic proteins from immune recognition and allows targeted conjugation without crosslinking. While PEGylation may reduce the activity of some proteins, the increased circulation time helps maintain effective drug levels in the bloodstream. The success of PEGylation in enhancing drug efficacy and safety is well-documented, with its impact continuing to shape pharmaceutical innovation.[24], [25]
Limitations of PEGylation and Innovations in Protein Delivery[26], [27], [28]
Although PEGylation has proven effective in enhancing the pharmacokinetics of protein-based therapeutics, it has some drawbacks, including limited biodegradability and the potential to alter or reduce protein activity. In response, Duncan et al. introduced polymer-masking-unmasking protein therapy (PUMPT), a novel method that uses biodegradable dextrin, a natural polysaccharide, to mask protein activity during transit and restore it at the target site through controlled degradation. In this approach, dextrin is chemically modified via succinoylation to provide reactive sites for covalent attachment. During degradation, the non-toxic byproducts maltose and isomaltose are generated in the presence of α-amylase. Testing showed that dextrin conjugation reduced trypsin activity by 34-69%, depending on molecular weight and modification level, but incubation with α-amylase restored 92-115% of the enzyme’s activity. PUMPT presents a promising solution for delivering proteins that are prone to inactivation or toxicity during transport, though further research is required to optimize the process and fully understand the degradation products to ensure safety.
Polymer-Drug Conjugates: Advancing Therapeutics[29], [30], [31]
Polymer-drug conjugates, where small-molecule drugs are attached to polymer carriers, represent a significant advancement in drug delivery, particularly in cancer treatment. This field began with the pioneering work of Ringsdorf in 1975 and was further developed by Duncan and Kopecek, who designed the first polymer-based anticancer drug conjugates to enter clinical trials. Unlike conventional drugs, which may cause widespread side effects by dispersing throughout the body, polymer-drug conjugates improve targeting by enhancing circulation time and using endocytosis for cellular uptake. Additionally, these conjugates leverage the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect to accumulate selectively in tumors.
A notable study by Satchi-Fainaro et al. explored an HPMA-TNP-470 conjugate, where the antiangiogenic drug TNP-470 was linked to an HPMA copolymer through an enzyme-cleavable GFLG tetrapeptide bond. This bond allows the drug to be released inside lysosomes by cysteine proteases, such as cathepsin B, which are abundant in many tumors. In animal studies, the conjugate accumulated in tumor tissues via the EPR effect and prolonged TNP-470’s therapeutic activity without the neurotoxic effects observed with the free drug, likely due to the conjugate’s inability to cross the blood-brain barrier. The HPMA-TNP-470 conjugate, currently in preclinical development under the name caplostatin by SynDevRx, has shown significant promise in cancer therapy.[32], [33], [34]
Emerging Polymer Architectures for Drug Delivery
Innovations in polymer chemistry have led to new architectures, such as dendrimers, star-shaped polymers, and grafted systems, for future drug delivery applications. For example, researchers studied the conjugation of paclitaxel, a poorly soluble chemotherapy drug, with linear bis-PEG and dendritic polyamidoamine (PAMAM) G4 to assess the impact of carrier structure on drug performance. Both PEG and PAMAM improved the solubility of paclitaxel compared to its free form (0.3 mg/ml). However, the PAMAM-based conjugate achieved a solubility of 3.2 mg/ml, outperforming the PEG-based system at 2.5 mg/ml. Confocal microscopy revealed that both conjugates achieved more uniform distribution within cells compared to free paclitaxel. While PEG reduced paclitaxel’s efficacy by 25-fold, the PAMAM-G4 dendrimer enhanced its anticancer activity by more than ten times, demonstrating the potential of dendrimers as superior carriers for intracellular delivery of poorly soluble drugs.
Classification of Polymers[35]
Polymers used in pharmaceutical applications can be categorized as follows:
Based on interaction with water
Non-biodegradable hydrophobic polymers (e.g., polyvinyl chloride)
Soluble polymers (e.g., HPMC, PEG)
Hydrogels (e.g., polyvinylpyrrolidone)
Based on polymerization method
Addition polymers (e.g., alkane polymers)
Condensation polymers (e.g., polystyrene, polyamides)
Based on polymerization mechanism
Chain polymerization
Step-growth polymerization
Based on chemical structure
Activated carbon-carbon polymers
Inorganic polymers
Natural polymers
Based on occurrence
Natural polymers (e.g., collagen, keratin, cellulose)
Synthetic polymers (e.g., polyesters, polyamides)
Based on bio-stability
Biodegradable polymers (e.g., lactides, glycolides, polyanhydrides)
Non-biodegradable polymers (e.g., acrolein, epoxy polymers)
Role of Polymers in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery [36]
Polymers are essential components in immediate-release dosage forms, such as tablets, where they act as excipients to aid manufacturing and protect drugs from degradation during storage. Microcrystalline cellulose is commonly used as a diluent in low-dose tablet formulations, offering an alternative to carbohydrate-based fillers. Polymers also serve critical roles in controlling drug release, enhancing solubility, and improving the stability of pharmaceutical formulations, making them indispensable for modern drug delivery systems.
Role of Polymers in Immediate-Release Dosage Forms [37], [38]
In tablet formulations, starch and cellulose function as disintegrants. Upon contact with water, these materials swell, causing the tablet to break apart and expose a larger surface area of the drug, improving its dissolution. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) act as binders, facilitating the formation of granules that enhance the flow and compressibility of the tablet mixture before compression. In some cases, tablets are coated with non-functional polymer films to protect the drug from degradation, mask unpleasant tastes, or improve the visual appearance of the product without altering the drug release profile.
Capsules as an Alternative Dosage Form [39], [40], [41], [42]
Capsules offer an alternative to tablets, particularly for drugs that are difficult to compress or have a bitter taste. They may also enhance bioavailability for certain drugs. Many polymeric excipients used in capsule formulations are the same as those found in immediate-release tablets. Traditionally, gelatin has been the primary material for both hard (two-piece) and soft (one-piece) capsules, but HPMC is now being widely adopted for hard capsules as a plant-based alternative.
Modified-Release Dosage Forms [43]
Immediate-release formulations can sometimes lead to ineffective treatment or unwanted side effects. To address these limitations, pharmaceutical scientists have developed modified-release systems, which improve therapeutic outcomes by controlling the release rate of the drug.
Extended-Release Dosage Forms[44]
For drugs with short half-lives, extended-release formulations help maintain therapeutic drug levels over an extended period, reducing dosing frequency and improving patient adherence. Common polymers used for extended-release systems include ammonium ethacrylate copolymers (Eudragit RS and RL), ethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate, and polyvinyl acetate. Eudragit RS is less water-permeable due to its higher content of quaternary ammonium groups. Additionally, ethyl cellulose is available in various viscosity grades, with higher viscosities forming stronger, more durable coatings.
Gastroretentive Dosage Forms[44]
Gastroretentive systems provide an alternative method for extended drug release by remaining in the stomach for longer periods. This approach ensures the drug dissolves in the stomach’s contents and gradually moves into the small intestine. Unlike traditional extended-release formulations, which release the drug throughout the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, gastroretentive systems are particularly useful for drugs absorbed primarily in specific GI regions. For example, some drugs are poorly absorbed from the distal gut, where conventional extended-release formulations may spend a significant amount of time. Researchers are exploring mucoadhesive and low-density polymers to increase gastric retention by either adhering to the stomach lining or floating on the stomach’s contents, but these strategies still face challenges in achieving consistent results.
Characteristics of an Ideal Polymer [43], [44]
Versatility: Should exhibit diverse mechanical, physical, and chemical properties
Non-Toxicity: Must be safe for administration with adequate mechanical strength
Cost-Effectiveness: Should be affordable and easy to manufacture
Biocompatibility: Must be inert and compatible with biological tissues and the environment
Criteria for Polymer Selection [44]
Solubility and Synthesis: The polymer should dissolve easily and be straightforward to synthesize
Molecular Weight: Must have a specific molecular weight to ensure desired functionality
Biocompatibility: Should not elicit adverse biological responses
Biodegradability: The polymer should break down safely in the body
Drug Linkage: Must offer stable and effective drug-polymer binding
Conclusion
Drug delivery systems are essential for the effective and safe administration of pharmaceutical compounds, playing a critical role in optimizing the release profile, absorption, distribution, and elimination of drugs. These systems not only enhance therapeutic efficacy but also minimize side effects, making them pivotal in modern medicine. The integration of various drug delivery solutions, such as oral, parenteral, pulmonary, nasal, transmucosal, and transdermal systems, further improves patient compliance and convenience.
Polymers play a crucial role in these developments thanks to their versatility and flexibility, enabling the creation of cutting-edge drug delivery systems. A variety of both natural and synthetic polymers, encompassing both biodegradable and non-biodegradable varieties, have broadened the scope for controlled and targeted drug release. Recent progress in polymer science and drug delivery methods has resulted in the emergence of more effective and patient-centric therapeutic solutions.
By meticulously selecting and engineering polymers, researchers can significantly enhance the performance of pharmaceutical compounds, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and the continued advancement of the medical field.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- . Biotechnology/Biotech Business, Policy, Law, and Science. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- . . 2008. [Google Scholar]
- O Pillai, R Panchagnula. Polymers in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2001. [Google Scholar]
- RL Reis, AM Cunha, PS Allan, MJ Bevis. Mechanical behaviour of injection-moulded starch-based polymers. Polym Adv Technol 1996. [Google Scholar]
- BL Seal, TC Otero. Polymeric biomaterials for tissue and organ regeneration. Mater Sci Eng Rep 2001. [Google Scholar]
- D Martino, A Sittinger, M Risbud. Chitosan: a versatile biopolymer for orthopaedic tissue-engineering. Biomaterials 2005. [Google Scholar]
- SB Lee, YH Kim, MS Chong, SH Hong, YM Lee. Study of gelatin containing artificial skin V: Fabrication of gelatin scaffolds using a salt leaching method. Biomaterials 2005. [Google Scholar]
- A K Mohanty, M Misra, G Hinrichsen. Biodegradable polymers and bio composites: An overview. Macromol Mater Eng 2000. [Google Scholar]
- M Clochard, E Dinand, S Rankin, S Simic, S Brocchini. New strategies for polymer development in pharmaceutical science: a short review. J Pharm Pharmacol 2001. [Google Scholar]
- V V Mody. Introduction to Polymeric Drug Delivery. Internet J Med Update 2010. [Google Scholar]
- M Clochard, E Dinand, S Rankin, S Simic, S Brocchini. New strategies for polymer development in pharmaceutical science: a short review. J Pharm Pharmacol 2001. [Google Scholar]
- O Pillai, R Panchagnula. Polymers in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2001. [Google Scholar]
- SP Vyas, RK Khar. . Controlled Drug Delivery: Concepts and Advances. 2002. [Google Scholar]
- M Reja, MA Quadir, SS Haider. Comparative evaluation of plastic, hydrophobic and hydrophilic polymers as matrices for controlled release drug delivery. J Pharm Sci 2003. [Google Scholar]
- AS Hoffman. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2002. [Google Scholar]
- JH Park, ML Ye, K Park. Biodegradable polymers for microencapsulation of drugs. Molecules 2005. [Google Scholar]
- GV Savage, CT Rhodes. The sustained release coating of solid dosage forms: a historical review. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 1995. [Google Scholar]
- A Abuchowski, JR Mccoy, NC Palczuk, TV Es, FF Davis. Effect of covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol on immunogenicity and circulating life of bovine liver catalase. J Biol Chem 1977. [Google Scholar]
- A Abuchowski, TV Es, NC Palczuk, FF Davis. Alteration of immunological properties of bovine serum albumin by covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol. J Biol Chem 1977. [Google Scholar]
- R Duncan. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003. [Google Scholar]
- R Duncan. Polymer conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Nat Rev Cancer 2006. [Google Scholar]
- JM Harris, RB Chess. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003. [Google Scholar]
- MJ Roberts, MD Bentley, JM Harris. Chemistry for peptide and protein PEGylation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2002. [Google Scholar]
- JM Harris, RB Chess. Effect of pegylation on pharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003. [Google Scholar]
- FM Veronese, A Mero. The impact of PEGylation on biological therapies. Biodrugs 2008. [Google Scholar]
- R Duncan, HRP Gilbert, RJ Carbajo, MJ Vicent. Polymer masked-unmasked protein therapy. 1. Bioresponsive dextrin-trypsin and -melanocyte stimulating hormone conjugates designed for α-amylase activation. Biomacromolecules 2008. [Google Scholar]
- H Ringsdorf. Structure and properties of pharmacologically active polymers. J Polym Sci Part C 1975. [Google Scholar]
- R Duncan, J Kopecek. Soluble synthetic-polymers as potential drug carriers. Adv Polym Sci 1984. [Google Scholar]
- R Duncan, JB Lloyd, J Kopecek. Degradation of sidechains of N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide copolymers by lysosomal enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1980. [Google Scholar]
- J Khandare, T Minko. Polymer-drug conjugates: progress in polymeric prodrugs. Prog Polym Sci 2006. [Google Scholar]
- J Kopeček, P Kopečková, T Minko, ZR Lu. HPMA copolymer-anticancer drug conjugates: design, activity, and mechanism of action. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2000. [Google Scholar]
- RS Fainaro, M Puder, JW Davies, HT Tran, DA Sampson. Targeting angiogenesis with a conjugate of HPMA copolymer and TNP-470. Nat Med 2004. [Google Scholar]
- L Chesler, DD Goldenberg, IT Seales, RS Satchi-Fainaro, M Grimmer. Malignant progression and blockade of angiogenesis in a murine transgenic model of neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 2007. [Google Scholar]
- R Satchi-Fainaro, R Mamluk, L Wang, S M Short, J A Nagy. Inhibition of vessel permeability by TNP-470 and its polymer conjugate, caplostatin. Cancer Cell 2005. [Google Scholar]
- JJ Khandare, S Jayant, A Singh, P Chandna, Y Wang. Dendrimer versus linear conjugate: influence of polymeric architecture on the delivery and anticancer effect of paclitaxel. Bioconjug Chem 2006. [Google Scholar]
- KJ Gandhi, SV Deshmane, KR Biyani. Comparative evaluation of plastic, hydrophobic and hydrophilic polymers as matrices for controlled release drug delivery. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MA Longer, HS Ch’ng, JR Robinson. Bioadhesive polymers as platforms for oral controlled drug delivery III: oral delivery of chlorothiazide using a bioadhesive polymer. J Pharm Sci 1985. [Google Scholar]
- K Park, JR Robinson. Bioadhesive polymers as platforms for oral-controlled drug delivery: method to study bioadhesion. Int J Pharm 1984. [Google Scholar]
- HS Chang. Bioadhesive polymers as platforms for oral controlled drug delivery II: synthesis and evaluation of some swelling, water-insoluble bioadhesive polymers. J Pharm Sci 1985. [Google Scholar]
- D Harris, JT Fell, H L Sharma, DC Taylor. Gastrointestinal transit of potential bioadhesive formulations in man: a scintigraphic study. J Control Rel 1990. [Google Scholar]
- S Leung, JR Robinson. Polymer structure features contributing to Mucoadhesion II. J Control Rel 1990. [Google Scholar]
- J Timmermans, AJ Moes. How well do floating dosage forms float. Int J Pharm 1990. [Google Scholar]
- L Whitehead. Floating dosage forms: an in-vivo study demonstrating prolonged gastric retention. J Controlled Rel 1998. [Google Scholar]
- JJ Marler, J Upton, R Langer, JP Vacanti. Transplantation of cells in matrices for tissue regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Novel Drug Delivery Systems
- Role of Polymers in Drug Delivery
- Non-Biodegradable Polymers:
- Others
- Functions of Polymers in Drug Delivery [17], [18]
- Polymer Therapeutics and PE Gylation [19], [20]
- Limitations of PEGylation and Innovations in Protein Delivery[26], [27], [28]
- Polymer-Drug Conjugates: Advancing Therapeutics[29], [30], [31]
- Emerging Polymer Architectures for Drug Delivery
- Classification of Polymers[35]
- Based on interaction with water
- Based on polymerization method
- Based on polymerization mechanism
- Based on chemical structure
- Based on occurrence
- Based on bio-stability
- Role of Polymers in Pharmaceutical Drug Delivery [36]
- Role of Polymers in Immediate-Release Dosage Forms [37], [38]
- Capsules as an Alternative Dosage Form [39], [40], [41], [42]
- Modified-Release Dosage Forms [43]
- Extended-Release Dosage Forms[44]
- Gastroretentive Dosage Forms[44]
- Characteristics of an Ideal Polymer [43], [44]
- Criteria for Polymer Selection [44]
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
