- Visibility 27 Views
- Downloads 3 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpca.2024.033
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Clinical pharmacology functional disorders of narcolepsy in central nervous system
Introduction
A rare neurological condition called narcolepsy is caused by a selective loss or malfunction of orexin (also called hypocretin) neurons in the lateral hypothalamus. Cataplexy and extreme daytime sleepiness are hallmarks of narcolepsy type 1 (NT1), which is also marked by sleep-wake symptoms such hallucinations, sleep paralysis, and disturbed sleep. The following clinical characteristics and biomarkers are used to support the diagnosis: positivity for HLA-DQB1*06:02, cerebrospinal fluid orexin insufficiency, and evidence of rapid eye movement sleep phases immediately after the commencement of sleep.
Stimulant and antiataplectic medication therapy is typically effective for treating symptoms. This review focuses on how genetic, environmental, and immune-related variables interact to cause a noticeable (but not unique) orexin signaling deficit in NT1 patients. Present are data that support the idea that narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) is a hypothalamic condition that affects not only sleep-wake but also motor, mental, emotional, cognitive, metabolic, and autonomic functions, as well as questions about the "narcoleptic borderland," which includes narcolepsy type 2 (NT2). Narcolepsy's current diagnostic criteria have some drawbacks, and a potential new classification scheme that includes borderland disorders is proposed. The developments and challenges in the causes and symptomatic treatment of narcolepsy are covered in the end.[1]
With a detailed description of a patient with excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep attacks, and episodes of muscle weakness brought on by emotions, Gélineáu originally created the word "narcolepsy" in 1880. Narcolepsy is defined by "excessive daytime sleepiness that is typically associated with cataplexy (i.e., narcolepsy with cataplexy) and/or with abnormal rapid eye movement (REM) sleep phenomena such as sleep paralysis and hypnagogic hallucinations," according to the current international classification. Although narcolepsy is a persistent neurological illness, it does not worsen over time.[2], [3] In diverse ethnic groups, narcolepsy affects 0.03 to 0.16% of the general population.[4], [5] It is an under diagnosed sleep condition. However, genetic predisposition and environmental factors are significant for the development of narcolepsy, and a few family cases of human narcolepsy (up to 5%) have also been described.[6] The majority of cases of human narcolepsy are sporadic. Pharmacological substances are used primarily to treat narcolepsy. Central nervous system (CNS) stimulants and/or modafinil are commonly used to treat EDS, and while these drugs are successful at reducing daytime sleepiness, they have little impact on cataplexy, hypnagogic hallucinations, and sleep paralysis.[7] One of the most popular anti-catataplectic medications, antidepressants reduce cataplexy and aberrant REM sleep patterns but have minimal impact on EDS.[7] A recently authorized hypnotic (or novel chemical), sodium oxybate, successfully manages cataplexy and aids in reducing daytime sleepiness. Based on the identification of narcolepsy genes in animals, the primary pathophysiology of human narcolepsy has recently been clarified. The genes implicated in the etiology of narcolepsy (hypocretin/orexin ligand and its receptor) in animals have been identified using forward (positional cloning in canine narcolepsy) and reverse (mouse gene knockout) genetics.[8], [9] Novel hypothalamic neuropetides called hypocretins and orexins are also engaged in a number of hypothalamic activities, including energy balance and neuroendocrine functions.[10], [11] Humans seldom have mutations in genes associated to hypocretin, but hypocretin-ligand insufficiency is frequently observed.[12], [13], [14] and this is clinically evident by undetectable or low levels of hypocretin in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).[13], [14], [15] This discovery will probably result in the creation of fresh diagnostic procedures and focused therapeutic approaches. In fact, the second version of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD) [16] added low CSF hypocretin levels (below 30% of the mean control value) to the diagnostic criteria for narcolepsy. Hypocretin-deficient narcolepsy now looks to be a more complex condition than just a simple sleep disorder because hypocretins are engaged in a variety of hypothalamic processes. An overview of the clinical features of human narcolepsy is given first, followed by those in the canine model, an update on the pathophysiology of narcolepsy (with a focus on the function of the hypocretins), and pharmacological treatments for narcoleptic symptoms and their mechanisms. Lastly, the anticipations for the future narcolepsy research will also be discussed.
Aetiology
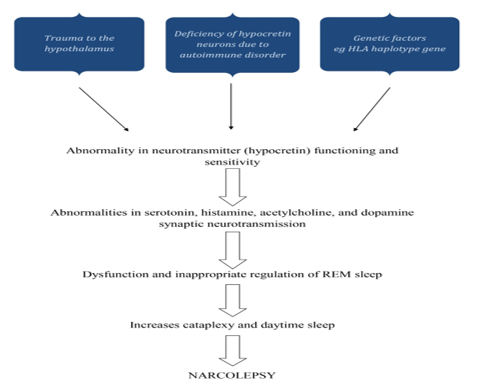
The idea that narcolepsy may have an infectious or post-traumatic etiology was first put forth in the 1920s. Evidence linking narcolepsy to the HLA system in the early 1980s raised the possibility that the immune system was involved in its etiology. Orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus were selectively lost when low CSF levels of orexin A were found in narcolepsy patients, suggesting that these cells may be the focus of such a process. Small neuropeptides called orexin A and orexin B stimulate target neurons by binding to orexin receptors of type 1 and type 2, respectively. The loss of this vital system causes many frontal, limbic, diencephalic, and brainstem networks to malfunction, which causes narcolepsy symptoms. This dysfunction has been described as a condition of instability or lack of boundary control that shows up as an inappropriate occurrence of sleep phenomena during awake and vice versa as well as an inability to maintain sleep or wake states for the right amount of time.
As a result, narcolepsy sufferers experience brief bursts of alertness and sleep, REM sleep atonia during waking (cataplexy), and dreaming (hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations) at sleep-wake and wake-sleep transitions. Orexin levels in CSF can be low or absent in patients with hypothalamic damage who do not have narcolepsy or cataplexy symptoms, suggesting that a deficiency in orexin production is neither (always) necessary nor (always) sufficient to cause narcolepsy in humans. However, there are patients with narcolepsy with and without cataplexy who have normal CSF levels of orexin.
The co-occurrence of genetic predisposition, environmental variables, and triggering events is now thought to be the cause of narcolepsy. This results in the selective immune-mediated death, malfunction, or silencing of orexin-producing neurons. In one study, part of the authors of this review reported the discovery of auto reactive CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in NT1 and NT2, which was published in 2018. A critical involvement for certain T lymphocytes in the neuronal damage found in human narcolepsy has been shown by three following findings, all of which were recently published. These reports offer additional support for this idea. Unless otherwise noted, the discussion that follows is focused on NT1. [17]
Epidemiology
Three dizygotic twins who were discordant for the condition and had no family history of the condition had their narcolepsy diagnosis confirmed. Two of them were female (aged 43 and 52, with UNS scores of 28 and 39), and one male (aged 55, with UNS score 20). Thus, 26/100,000 or 0.026% of the study population had narcolepsy (with a 95% confidence interval of 0-56/100,000; 27). In Finland, there were 3.73 million people who were 20 years of age or older by the end of 1990. Of these, 1.91 million were between the ages of 33 and 60. As a result, the latter age group would have roughly 500 narcoleptics (or, using the upper 95% confidence limit, approximately 1,100 narcoleptics). The total number of narcoleptics among adults in Finland may be around 1,000, and if the figure is based on the upper 95% confidence limit, there would be about 2,100 narcoleptics, given that the onset of narcolepsy typically occurs at the age of 20. [18]
Future of Epidemiology of Nacrolepsy
Awareness of the severity and prevalence of narcolepsy has dramatically increased with the rapid advancement of diagnostic and therapeutic tools. In this way, knowledge of narcolepsy's results and signs among the general population is growing. With the aid of an understanding of the disease's epidemiology, scientists should be able to concentrate on the social, behavioral, genetic, and environmental processes and impacts of the illness. Nevertheless, narcolepsy is still so uncommon that many people are unaware of the disorder or where to find treatment, despite scientific advancements. At the clinical level, a person's quality of life and everyday functioning are their main concerns. Narcolepsy has effects on public health and safety since its victims are more likely to nod off behind the wheel. To the best of our understanding, the disease has no preference for some socially disadvantaged populations over others in terms of social disparities. However, due of high rates of non-conclusion, mis-conclusion, or delayed determination, there is a concern that those who do not seek medical care are not receiving enough treatment or conclusion. Furthermore, due of the problems they confront in social and professional situations as a result of their disease, people with narcolepsy may be more likely to fall through the cracks. Burdened populations, particularly the unemployed, who do not have as much access to health care, should be considered at a higher risk of having undetected cases of narcolepsy. With greater epidemiological study on narcolepsy, the scientific and medical communities can enhance the disease's causes, awareness, early identification, and treatment.
Pathophysiology
Normal sleep is a structured process separated into two distinct states: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-REM sleep (NREM). NREM sleep is distinguished by slow oscillations of thalamocortical neurons, which are partially detectable as cortical slow waves. In humans, NREM sleep is split into four stages (S1, S2, S3, and S4) based on distinctive electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. Human sleep alternates between NREM phases S1 to S4, followed by REM sleep; this sleep cycle occurs every 90 minutes and is repeated 4 to 5 times per night. During a typical night's sleep, there is a shift from a prevalence of slow-wave NREM sleep in the first half of the night to a predominance of REM sleep in the second half of the night. It is theorized that sleep involves interactions between brain areas that facilitate sleep and hinder arousal. An ascending arousal route that begins in the rostral pons and goes into the mid brain reticular formation promotes wakefulness. Acetylcholine, nor-epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, histamine, excitatory aminoacids, andorexin/hypocretin-producing neurons in the brain stem and hypothalamus may be involved. These neurotransmitters are also thought to be involved in the regulation of muscle tone while sleeping. Each of these arousal networks can promote wakefulness, but total alertness and brain engagement need coordinated action. During sleep, a switch in the hypothalamus turns off the arousal system. Narcolepsy is a significant neurologic dysfunction of this control system. Over the last 40 to 50 years, we have gained a better understanding of the pathologic mechanisms of narcolepsy. Many of its characteristics were linked to REM sleep disruption in the 1960s; particularly, those with narcolepsy entered REM sleep more rapidly when falling asleep than those without narcolepsy. This is known as a sleep onset REM period (SOREMP) or shortened REM sleep latency. This transition to REM sleep can occur shortly after falling asleep, without first entering NREM sleep. Cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations are all symptoms of REM sleep incursion into awake in narcolepsy. However, cataplexy is pathognomonic for narcolepsy, but SOREMPs, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations are frequently seen in other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea syndromes, or even in normal populations when their sleep patterns are disrupted.[19]
Diagnosis
Your doctor may suspect narcolepsy based on symptoms such as extreme daytime sleepiness and an abrupt loss of muscular tone, known as cataplexy. Your doctor will almost certainly send you to a sleep specialist. For a formal diagnosis, an overnight visit at a sleep facility is required for a full sleep investigation.
A sleep specialist will most likely diagnose narcolepsy and determine its severity based on the following criteria:
Your sleeping habits
A comprehensive sleep history may aid in diagnosis. You'll most likely complete the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. This scale includes brief questions to assess your level of tiredness. You rate your likelihood of falling asleep at specific times, such as sitting down after lunch.
Your sleep logs
You may be asked to record your sleeping habits for a week or two. This allows your provider to compare how your sleep habits may connect to your level of alertness. Your doctor may also request that you wear an actigraph. This device is worn on the wrist like a watch. It tracks activity and rest periods. It gives an indirect indication of how and when you sleep.
Polysomnography is a type of sleep study
This test uses flat metal discs called electrodes that are implanted on your skull to measure impulses while you sleep. You will need to spend one night in a medical facility for this test. The test detects brain waves, heart rate, and breathing patterns. It also tracks your eye and leg movements.
Multiple sleep latency tests are performed
This test determines the amount of time it takes you to fall asleep during the day. In the sleep facility, you will be required to take four or five naps. Each snooze should be separated by two hours. Your sleep patterns will be monitored by the professional. People with narcolepsy can readily fall asleep and enter rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
Genetic testing as well as lumbar puncture, sometimes known as a spinal tap
Genetic testing can sometimes be used to determine if you are at risk for type 1 narcolepsy. If this is the case, your sleep specialist may advise you to have a lumbar puncture to evaluate the level of hypocretin in your spinal fluid. This test is only performed in specialized facilities.
These tests can also assist in ruling out other potential reasons of your symptoms. Inadequate sleep, the use of sedating drugs, and sleep apnea can all contribute to excessive daytime sleepiness. [20]
Symptoms
During the first several years of narcolepsy, symptoms may worsen. They then continue for the rest of their lives. These are some examples:
Excessive daytime sleepiness
Narcolepsy causes people to fall asleep suddenly. It can happen anywhere and at any time. It might happen when you're bored or throughout a task. For example, you could be working or talking with friends when you suddenly fall asleep. It is extremely dangerous if you fall asleep while driving. You could fall asleep for a few minutes or up to a half-hour. You'll often feel invigorated after waking up, but then you'll fall back asleep. You may also feel less awake and attentive during the day. Daytime sleepiness is frequently the first symptom to manifest. It is difficult to focus and function when you are drowsy.
When persons with narcolepsy fall asleep briefly, they may continue working on a task. You could, for example, fall asleep while writing, typing, or driving. You may continue to work on the task while sleeping. You can't recall what you did when you wake up, and you probably didn't do it properly.
Muscle tone suddenly drops
Cataplexy is the medical term for this condition. It might induce slurred speech or total muscular paralysis. Symptoms can linger for many minutes. Cataplexy is uncontrollable. It is prompted by strong emotions. Cataplexy is frequently caused by good feelings. Symptoms may be triggered by laughter or enthusiasm. However, muscle tone can be lost due to fear, surprise, or rage. When you laugh, for example, your head may slump without your control. Alternatively, your knees could abruptly lose strength, causing you to tumble. Some narcoleptics only have one or two episodes of cataplexy per year. Others have multiple episodes per day. These symptoms do not occur in every case of narcolepsy. Paralysis caused by sleep. Sleep paralysis is a common symptom of narcolepsy. You can't move or speak when falling asleep or waking up if you have sleep paralysis. It is typically transient, lasting only a few seconds or minutes. However, it can be frightening. You may be aware of what is happening and recollect it later.
Narcolepsy does not affect everyone who has sleep paralysis.
Hallucinations
During sleep paralysis, people may see things that aren't there. Hallucinations can occur in the absence of sleep paralysis. If they occur while you fall asleep, they are referred to as hypnagogic hallucinations. If they occur upon awakening, they are known as hypnopompic hallucinations. For example, you may have the impression that there is a stranger in your bedroom. Because you may not be entirely asleep when you begin dreaming, these hallucinations may be vivid and terrifying.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep changes
The majority of dreams occur during REM sleep. REM sleep usually begins 60 to 90 minutes after falling asleep. However, patients with narcolepsy frequently transition to REM sleep more quickly. Within 15 minutes of falling asleep, they usually enter REM sleep. REM sleep can occur at any time of day.[20]
Regimen f Narcolepsy
With medication for
CNS stimulant
Antidepressants drugs
SARR drugs
Anti Depressantdrugs
Protriptyline
It is an Tricyclic antidepressant agents. Monoaminergic uptake blocker (Nor- epinephrine>5-HT>Dopamine). Anticholinergic effects; all antidepressants have immediate effects on cataplexy, but abrupt cessation of treatment can induce very severe rebound in cataplexy. [21]
Drug stimulate the CNS
Selegiline
A monoamine oxidase type B inhibitor, was shown to be effective for treating cataplexy and excessive daytime drowsiness [22] preferred first option for treating excessive daytime drowsiness, study has voiced some reservations due to the possibility of drug and dietary interactions [23]
Modafinil
Drugs that stimulate the central nervous system are primary treatment to help people with narcolepsy used mostly MODAFINIL. These medicines aren’t as habit-forming as older stimulants. Side effects are uncommon but may include headache, nausea or anxiety.
Pitolisant
Pitolisant is an N-piperidyl derivatives. It is the first non-imidazole-based H3R antagonist/inverse agonist. It also called as tiprolisant [24]
Pitolisant is the first FDA-approved drug to treat hypersomnolence in narcolepsy and it is mild stimulant [24] which is high-affinity competitive antagonist and an inverse agonist -half-maximal effective concentration and an inhibitor constant -high potency.
Mechanisms of Action
Pitolistant
Blockage of H3R has become a target in the management of disorders of hypersomnia, including narcolepsy.H3R’s is participating to control the release of histamine release.
It blocks the auto-inhibiting activity of histamine and H3R agonists on endogenous histamine release
Which decreases histamine release and Procedure CNS stimulant action.
At a low concentration of 100 nm, it has no significant interaction with almost a hundred other human receptors and channels. [25] It also increases acetylcholine release in the prefrontal cortex. Pitolisant preferentially increases dopamine in the prefrontal cortex but not in the striatal complex that comprises the nucleus accumbens [26]
Pharmacokinetics of Pitolisant
Administrated via the oral route, get Adsorbed on blood circulation , distribution over bound to the blood stream. Metabolism of pitolisant occurs under the action of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. metabolites are eliminated mainly through the urine (63%), expired air (25%) and in the feces (<3%).
Contraindications of pitolisant
Severe Hepatic impairment. Contraindicated women of reproductive potential on hormonal contraception should still use an alternative non hormonal contraceptive during and up until 21 days. In pregnancy, does cross the placenta and Produce to teratogenicity Effect on fetus. [27]
Drug interactions
Antihistamines and TCAs should be avoided as they may decrease the effect of pitolisant.[3]
CYP2D6 inhibitors drugs (qunindine and terbinafine) is increasing the serum conc. and reduce the dose of pitolisant.[28]
Amphetamines
It is belongs to brand (Adderall XR 10, Dexedrine, etc.) or METHYLPHENIDATE (Ritalin, Concerta, etc.) are prescribed for some patients. Although some medications work well, they can also be addictive. They could result in negative side effects like anxiety and a rapid heartbeat.
Sodium oxybate or oxybatesalts
These medicines work for relieving cataplexy. They help improve nighttime sleep, which is often poor in narcolepsy. They also may help control daytime sleepiness. It’s taken in two doses, one at bedtime and one up to four hours later. Xywav is a newer formulation with less sodium [29]
Future Therapy: Intranasal hypocretin-1 replacement is a therapy being developed that crosses the blood–brain barrier and appears to have a great potential for the treatment of narcolepsy [30] Animal studies have shown thioperamide, a histamine (H3) antagonist, may improve wakefulness by blocking histamine auto receptors. This therapy is currently being researched and aims to improve EDS in patients with narcolepsy. [31]
Nonpharmacologic regimen
To avoid alcohol and other
CNS-depressant drugs
To avoid the misperception of laziness or incompetence.
Good sleep hygiene should be part of a narcoleptic patient’s lifestyle [32]
Herbal regimen
Guarana natural stimulant
Cayenne pepper, Ginkgobiloba� increases blood flow to the brain
Ephedra Increases energy levels
Gotu kola educes fatigue
Rosemary tea, B complex vitamins important in the sleep-wake cycle
Self-Care and Natural Regimen for Narcolepsy
Acupuncture remedy
Strategic napping
Regular physical activity can help to reduce narcolepsy.(In, 2017 - 42 people with narcolepsy showed that cardio exercise is inversely related to episodes of muscular loss and sleepiness) [33]
Try a low carb diet
DFeel less sleepy during the day
Reduces episodes of involuntary sleep
Sleep paralysis [34]
Conclusion
A complicated, multifactorial sleep disease called narcolepsy is marked by hallucinations, cataplexy, and sleep paralysis. It is a condition of the central nervous system that affects a person's everyday activities and quality of life. The main goals of drug treatment for narcolepsy are to lessen symptoms, enhance sleep, and lessen the consequences of cataplexy. Armodafinil and other stimulants are regarded as first-line narcolepsy therapies for daytime sleepiness. By acting as stimulants, they aid in boosting the release of monoamines like dopamine and norepinephrine, which help promote alertness and decrease drowsiness. Another significant medication used to treat persistent insomnia and cataplexy is sodium oxybate. Both slow wave sleep and nighttime sleep are improved. It has been demonstrated that antidepressants, in particular SSNRIs, are useful in the treatment of cataplexy. These medications control the brain's neurotransmitter levels, which lessens the frequency and severity of strokes.
Drugs are not a cure for narcolepsy, but they have been demonstrated to be beneficial in addressing its side effects.
A mix of medications is frequently provided to treat the various disease symptoms, and the regimen plan is typically modified to the patient's needs. It is important to remember that the medication may have reactions and side effects that need to be watched by a doctor or healthcare professional. Future studies in the area of pharmacotherapy for narcolepsy should concentrate on creating various targeted treatments with enhanced long-term outcomes and safety. For the purpose of creating therapeutic alternatives and ultimately controlling this complicated CNS illness, it is also critical to comprehend the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying narcolepsy as well as to identify new pharmacological targets. Collaboration between scientists, doctors, and pharmaceutical companies will be crucial to improving our knowledge of narcolepsy and its treatment options.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- CL Bassetti, A Adamantidis, D Burdakov, F Han, S Gay, U Kallweit. Narcolepsy-clinical spectrum, aetiopathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol 2019. [Google Scholar]
- M Billiard, A Besset, J Cadilhac, C Guilleminault, E Lugaresi. The clinical and polygraphic development of narcolepsy. Epidemiology and longterm evolution 1983. [Google Scholar]
- K Sonka, M Tafti, M Billiard, S Smiru, M Frauceschi, L Ferini-Strambi. Narcolepsy and aging. Sleep and Aging 1991. [Google Scholar]
- C Guilleminault, Narcolepsy Syndrome, MH Kryger, T Roth. . Principles and practice of sleep medicine 1994. [Google Scholar]
- C Hublin, J Kaprio, M Partinene, M Koskenvuo, K Heikkila, S Koskimies. The prevalence of narcolepsy: an epidemiological study of the Finnish twin cohort. Ann Neurol 1994. [Google Scholar]
- T Tashiro, T Kanbayashi, Y Hishikawa. An epidemiological study of narcolepsy in Japanese. 1994. [Google Scholar]
- C Guilleminault, E Mignot, FC Grumet. Familial patterns of narcolepsy. Lancet 1989. [Google Scholar]
- S Nishino, E Mignot. Pharmacological aspects of human and canine narcolepsy. Prog Neurobiol 1997. [Google Scholar]
- RM Chemelli, JT Willie, CM Sinton, JK Elmquist, T Scammell, C Lee. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 1999. [Google Scholar]
- L Lin, J Faraco, R Li, H Kadotani, W Rogers, X Lin. The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell 1999. [Google Scholar]
- T Sakurai, A Amemiya, M Ishii, I Matsuzaki, RM Chemelli, H Tanaka. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998. [Google Scholar]
- L De Lecea, TS Kilduff, C Peyron, XB Gao, PE Foye, PE Danielson. The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998. [Google Scholar]
- S Nishino, B Ripley, S Overeem, GJ Lammers, E Mignot. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet 2000. [Google Scholar]
- S Nishino, B Ripley, S Overeem, S Nevsimalova, GJ Lammers, J Vankova. Low CSF hypocretin (orexin) and altered energy homeostasis in human narcolepsy. Ann Neurol 2001. [Google Scholar]
- C Peyron, J Faraco, W Rogers, B Ripley, S Overeem, Y Charnay. A mutation in a case of early onset narcolepsy and a generalized absence of hypocretin peptides in human narcoleptic brains. Nat Med 2000. [Google Scholar]
- E Mignot, GJ Lammers, B Ripley, M Okun, S Nevsimalova, S Overeem. The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias. Arch Neurol 2002. [Google Scholar]
- CL Bassetti, A Adamantidis, D Burdakov, F Han, S Gay, U Kallweit. Narcolepsy-clinical spectrum, aetiopathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol 2019. [Google Scholar]
- C Hublin, M Partinen, J Kaprio, M Koskenvuo, C Guilleminault. Epidemiology of narcolepsy. Sleep 1994. [Google Scholar]
- S Nishino. Narcolepsy: pathophysiology and pharmacology. J Clin Psych 2007. [Google Scholar]
- C Scott, MD Litin. . Mayo Clinic Family Health 2018. [Google Scholar]
- TJ Swick. Treatment paradigms for cataplexy in narcolepsy: past, present, and future. Nat Sci Sleep 2015. [Google Scholar]
- G Mayer, E Meier, K Hephata. Selegeline hydrochloride treatment in narcolepsy. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Neuropharmacol 1995. [Google Scholar]
- TI Morgenthaler, VK Kapur, T Brown. Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin. Sleep 2007. [Google Scholar]
- JC Schwartz. The histamine H3 receptor: from discovery to clinical trials with pitolisant. Br J Pharmacol 2011. [Google Scholar]
- YY Syed. Pitolisant: first global approval. Drugs 2016. [Google Scholar]
- B Setnik, M Mcdonnell, C Mills. Evaluation of the abuse potential of pitolisant, a selective H3-receptor antagonist/inverse agonist, for the treatment of adult patients with narcolepsy with or without cataplexy. Sleep 2019. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- DM Riddy, AE Cook, DM Shackleford. Drug-receptor kinetics and sigma-1 receptor affinity differentiate clinically evaluated histamine H(3) receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 2019. [Google Scholar]
- JT Guevarra, R Hiensch, AW Varga, DM Rapoport. Pitolisant to Treat Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Cataplexy in Adults with Narcolepsy: Rationale and Clinical Utility. Nat Sci Sleep 2020. [Google Scholar]
- . Oxybate salts (calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium). Facts & Comparisons eAnswers. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- KM Beusterien, AE Rogers, JA Walsleben. Health-related quality of life effects of modafinil for treatment of narcolepsy. Sleep 1999. [Google Scholar]
- AJ Barbier, C Berridge, AD Dugovic. Acute wake-promoting actions of JNJ-5207852, a novel, diamine-based H3 antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 2004. [Google Scholar]
- J Bhattarai. Current and future treatment options for narcolepsy: A review. Sleep Med 2017. [Google Scholar]
- M Matoulek. Cardiovascular fitness in narcolepsy is inversely related to sleepiness and the number of cataplexy episodes. Sleep Med 2017. [Google Scholar]
- AM Husain. Diet therapy for narcolepsy. Neurology 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Future of Epidemiology of Nacrolepsy
- Pathophysiology
- Diagnosis
- Your sleeping habits
- Your sleep logs
- Polysomnography is a type of sleep study
- Multiple sleep latency tests are performed
- Genetic testing as well as lumbar puncture, sometimes known as a spinal tap
- Symptoms
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Muscle tone suddenly drops
- Hallucinations
- Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep changes
- Regimen f Narcolepsy
- Anti Depressantdrugs
- Mechanisms of Action
- Pharmacokinetics of Pitolisant
- Contraindications of pitolisant
- Drug interactions
- Amphetamines
- Sodium oxybate or oxybatesalts
- Nonpharmacologic regimen
- Herbal regimen
- Self-Care and Natural Regimen for Narcolepsy
- Conclusion
- Source of Funding
- Conflict of Interest
